Microservices have become a buzzword in the startup world in recent years, with many companies claiming that they are the key to innovation and success. But are microservices really all they’re cracked up to be? In this blog, we’ll explore the latest trends in microservices adoption among startups, as well as some of the drawbacks of this approach. We’ll then try to figure out if microservices are worth the hype.
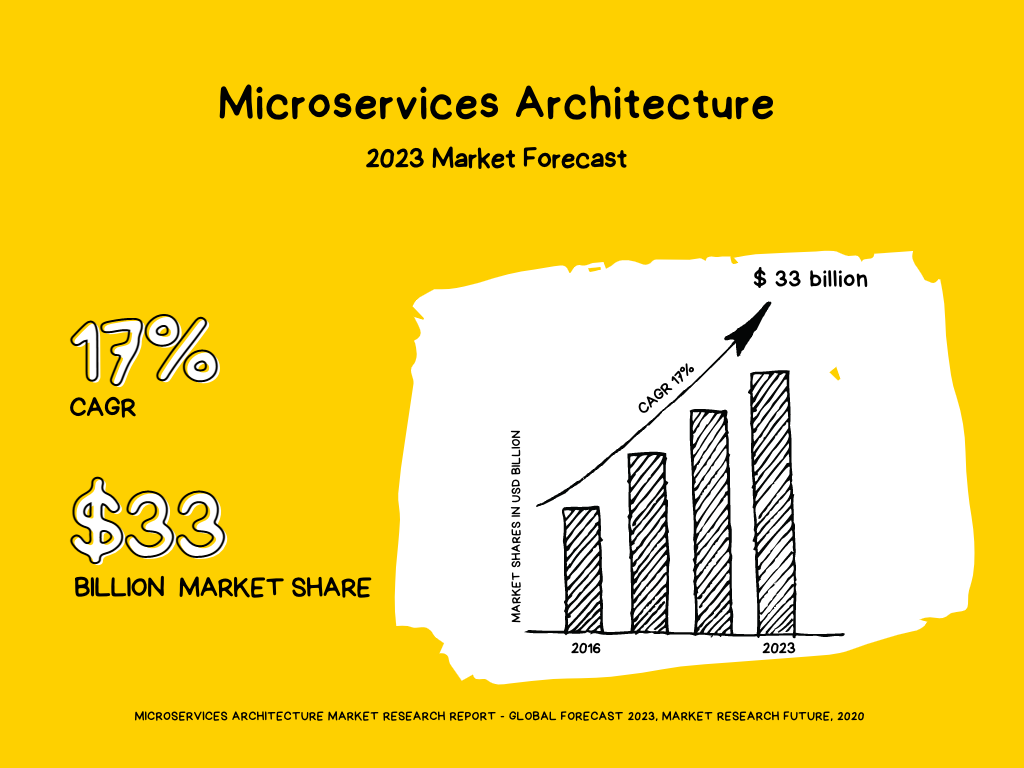
There is evidence to suggest that the adoption of microservices by companies is on the rise. According to market research, the microservices industry is expected to see a 17% growth from 2017 to 2023, reaching a value of $33 billion. This indicates that more and more companies are turning to microservices architecture to support their growth.
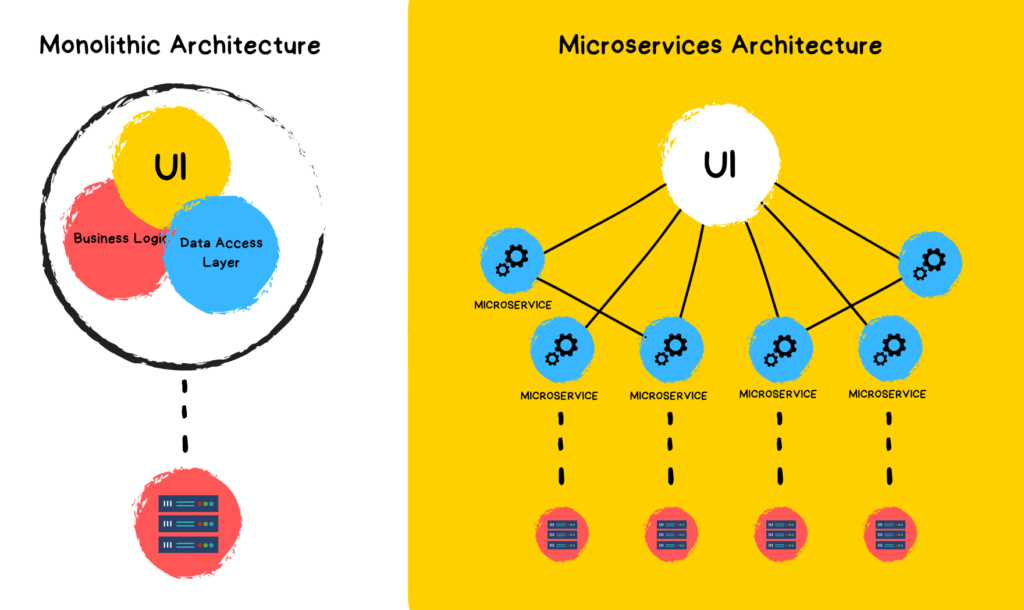
What are Microservices?
Before diving into the trends, let’s define exactly what we mean by microservices. Simply put, microservices are a software development approach that involves building a single application as a suite of small, independent services. These services communicate with each other using APIs and can be developed and deployed independently of one another.
The goal of microservices is to make it easier for developers to build and maintain complex applications, by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable pieces. This can lead to faster development times, as well as easier scalability and flexibility.
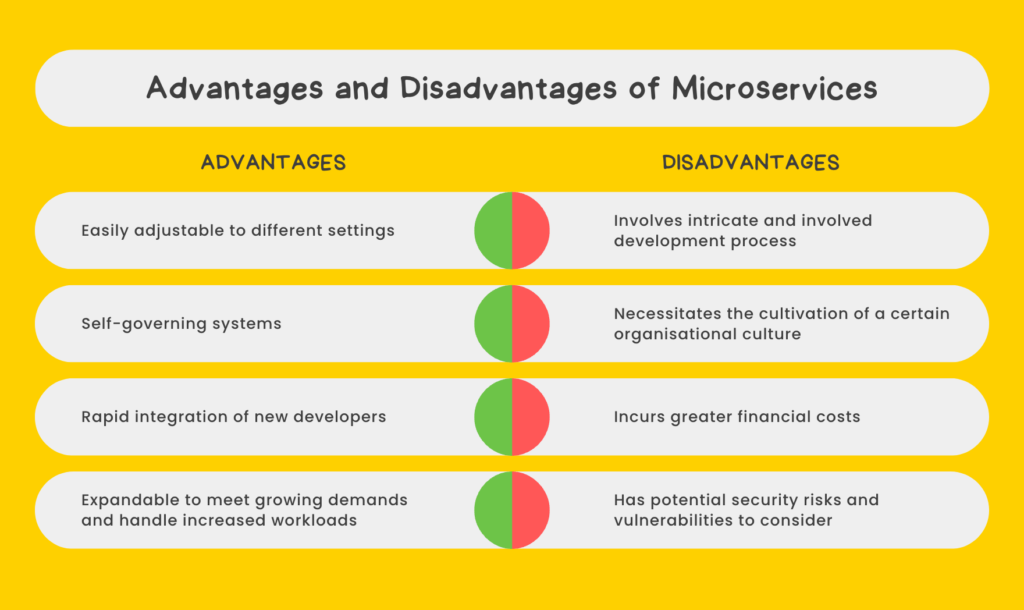
Advantages of Microservices
The advantages of microservices are many and varied. One of the main advantages is that it allows for faster development and deployment of new features and updates. By breaking the application down into smaller, independent services, developers can work on them in parallel, and deploy them as soon as they are ready. This can lead to faster time to market, which can be particularly useful for startups that are looking to get a product out the door quickly.
Another advantage of microservices is that it allows for better scalability and flexibility. Since each service is a self-contained unit, it can be scaled independently of the rest of the application. This makes it easier to add more resources to specific services as needed and can help to improve overall performance and availability.
In addition, microservices can also lead to more efficient resource usage, as each service can be deployed on the most appropriate infrastructure for its specific requirements. This means that resources aren’t wasted on services that don’t need them.
Overall, microservices have several advantages that can be leveraged by startups to support their growth and enable them to be more efficient, flexible, scalable and agile.
Drawbacks of Microservices
While microservices can provide a number of benefits, it’s important to be aware of some of the potential drawbacks as well. One of the biggest challenges with microservices is the increased complexity of managing a large number of independent services. This can make tracking issues and bugs more difficult, and can lead to increased communication and coordination requirements among team members.
Another potential drawback is the increased overhead in terms of resource requirements. Since each service is its own independent unit, it can require its own dedicated resources (such as servers and databases). This can lead to higher infrastructure costs, particularly for startups that are just getting off the ground.
Development time and Development cost of Microservices
One potential benefit of microservices is that they can lead to faster development times. Since each service is a self-contained unit, developers can work on them independently and deploy them as soon as they are ready, rather than waiting for the entire application to be completed. This can lead to faster time to market and can be particularly useful for startups that are looking to get a product out the door quickly.
However, it’s important to note that microservices can also potentially increase development costs. Since each service is its own independent unit, it can require its own dedicated resources (such as servers and databases). This can lead to higher infrastructure costs, particularly for startups that are just getting off the ground. In addition, managing a large number of independent services can also require more communication and coordination among team members, which can increase development overhead.
Overall, the impact of microservices on development cost and time will depend on a variety of factors, including the complexity of the application, the skills of the development team, and the resources available. It’s important for startups to carefully consider these trade-offs and weigh the potential benefits against the potential costs before deciding whether to adopt a microservices approach.
Microservices in Startups: The Latest Trends
So, what are the latest trends in microservices adoption among startups? Here are a few key points to consider:
- Increased Adoption: One of the biggest trends we’re seeing is a general increase in the number of startups adopting microservices. According to a recent survey, around 70% of startups are now using microservices in some form. This is up from just 50% a few years ago, indicating that more and more startups are recognizing the benefits of this approach.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Another trend we’re seeing is the use of cross-functional teams to develop and maintain microservices. This means that instead of having a separate team dedicated to each service, teams are composed of members with a variety of skills and expertise, who work together to build and manage the entire system.
- Cloud-Native: Many startups are also adopting a “cloud-native” approach to microservices, which involves building and running services natively on the cloud. This can provide a number of benefits, including increased scalability and reliability, as well as reduced infrastructure costs.
- DevOps Culture: Finally, we’re seeing a trend towards the adoption of a “DevOps” culture among startups using microservices. DevOps is a philosophy that emphasizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams and can be particularly useful in a microservices environment where teams are working on a large number of independent services.
Programming languages used for Microservices
There are many programming languages that can be used to develop microservices, some of the popular languages include

Java is one of the most popular languages for developing microservices. It is a high-performance, object-oriented language that is well suited for building scalable and reliable systems. Many microservices frameworks and libraries such as Spring Boot and Wildfly Swarm are built on Java.

Python is a versatile and easy-to-learn programming language that is well suited for building microservices. It has a large and active community, and many libraries and frameworks such as Flask, Django and FastAPI.

JavaScript has become more popular in recent years for developing microservices. It is a versatile language that can be used on both the front-end and back-end of web applications. Popular JavaScript frameworks such as Node.js and Express can be used to develop microservices.

Go is a relatively new language that was developed by Google. It is designed to be simple and efficient, and is well suited for developing high-performance microservices. It has native support for concurrency, making it a good choice for handling multiple requests simultaneously.

C# is a popular language for developing microservices on the .Net platform. It is a modern, object-oriented language that is well suited for building scalable and reliable systems. Popular .Net framework for developing microservices are ASP.NET Core
These are just a few examples of the programming languages that can be used to develop microservices, there are many other languages as well. The choice of language will depend on the specific needs of the project, as well as the skills and preferences of the development team.
Tools used for Microservices
There are many tools available for developing microservice architecture, including:
- API Management Tools: These tools are used to design, publish, and manage APIs, which are used to communicate between microservices. Examples include Apigee, Kong, and Tyk.
- Container Orchestration Tools: These tools are used to manage and deploy containerised microservices. Examples include Docker, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos.
- Service Mesh Tools: These tools are used to manage and monitor communication between microservices. Examples include Istio, Linkerd, and Consul.
- Monitoring Tools: These tools are used to monitor the performance and health of microservices. Examples include Datadog, New Relic, and AppDynamics.
- Testing Tools: These tools are used to test the functionality and performance of microservices. Examples include Postman, JUnit, and JMeter.
It’s important to note that the specific tools used will depend on the needs and preferences of the development team, as well as the language and platform being used.
Hip or Hype?
So, are microservices just a passing fad, or are they here to stay? In our opinion, microservices are definitely more than just hype. While they may not be the right solution for every startup, they can provide a number of benefits in terms of development speed, scalability, and flexibility. That being said, it’s important for startups to carefully consider whether microservices are the right fit for their specific needs, taking into account the potential drawbacks such as increased complexity and resource requirements. As with any new technology, it’s important to research and makes an informed decision before diving in.
An example of a company that has integrated the Microservice architecture into its system is Splice. Splice is a music production platform that allows users to create, collaborate on, and share music. The company has adopted a microservices architecture to manage the complexity of its application, which includes features such as real-time collaboration, audio processing, and music recommendation algorithms. By using microservices, Splice has been able to develop and deploy new features and updates more quickly, and has been able to scale its application more easily as they have grown.
Another example of a startup that is using microservices is a company called AccuRate. AccuRate is a fintech company that provides small businesses with on-demand access to working capital. The company has adopted a microservices architecture in order to separate its system into smaller, more manageable pieces. Accurrate using microservices allows them to scale their application as they’ve grown, and deploy new features more efficiently. They have several microservices including microservices for risk assessment, loan processing, identity verification and credit decision, this way each microservices can be developed and deployed independently, making the system more resilient, flexible and scalable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the trend towards microservices adoption among startups is definitely worth paying attention to. While they may not be the perfect solution for every company, they can provide a number of benefits for those who are able to make the most of them and are willing to invest the necessary time and resources. Whether you’re a startup looking to adopt microservices, or just curious about the latest trends, we hope this blog has provided some useful insights.
At Wolfpack, we also provide our clients with developing Microservices. For more information on Wolfpack and our offerings you can head on to our site at http://wolfpackdigi.com/mach-architecture/.
